Reasons why many use VPN, proxy, and onion services vary, but I believe the common reason is for privacy and anonymity.
The majority of those who use VPN, proxy, and onion services always think they are invisible, untraceable, and 100% secure. The question is, how protected and secure are you while using the above services?
Before we dive into how VPN, proxy, and onion services work and their security implications, I will like us to differentiate between two important terms: privacy and anonymity.
Privacy is the hiding of messages or data we transfer on the internet to improve confidentiality and prevent unauthorized intrusions, while anonymity is the hiding of the identity of the sender of a message or data on the internet. These two terms are important to note as we progress.
What is a VPN?
VPN stands for virtual private network. VPN is a service that encrypts your internet traffic and disguises your IP address from the server you are visiting.
The two important things you should note about VPN are:
1. It encrypts internet traffic. This means it turns the messages or information you are sending or transferring on the internet into gibberish. So that anyone who sees or intercepts it won’t be able to read it and understand it.
2. It disguises your IP address. An IP address is what your devices, like computers or phones, are identified with on the internet. Two people cannot have the same IP address at the same time.
Related Post: IP Address- What Can A Hacker Do With it?
So if you are visiting a website, your IP address will be known or logged by the website you visit. This helps the website owners identify you and also track your activities on their site. What a VPN does is act as an intermediary between you and the website you visit, preventing the website owners from seeing your IP address but that of the VPN server.
Related Post: How to Install Free VPN on Your Android Phone
How does a VPN work?
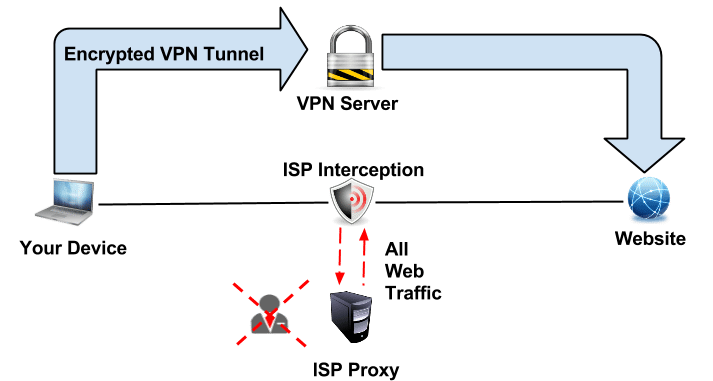
A VPN works as an intermediary between you and the services you visit on the open internet.
For instance, when you try to visit your bank websites using a VPN, what happens is that your request will first get encrypted and sent to your VPN host server through a tunnel, which will then redirect your request on your behalf to your bank. Now your bank will receive your request as if it were from the VPN server and not from you. Therefore, when your bank replies to the request, it sends the response to the VPN server, which in turn forwards it back to you.
What this implies is that you trust your VPN providers to have your information more than you trust your bank. This is because the VPN providers will see your IP address while your bank won’t. They will also know exactly the website you are visiting and the data you are sending if it is unencrypted.
How Does VPN Change Your Location?
Your location while using a VPN depends on the location of the VPN server you are using. Remember, your demographic location data is disclosed on the internet using your IP address. This is why your location can be tracked using your IP address.
Therefore, for VPN, your IP will be disguised as that of your VPN server. So, whenever you make a request to a website, the site will receive the requests from your VPN server on your behalf. They will be seeing your location as that of the server.
For instance, if you want to access your bank website in Biafra Land and you are using a VPN with a server located in the USA, what happens is that your Internet Service Provider in Biafra Land will relay your request to the VPN server in the USA first. Then Your VPN server will redirect the request back to Biafra Land as if it were coming from the USA. So, your bank will see it as if someone is accessing your bank account from the USA. Then, your bank will send the response back to the VPN server in the USA, which will then redirect the response back to you in Biafra.
With this example, you can see that the location change is due to the location of the VPN server.
Does your ISP know you are using a VPN?
ISP stands for Internet Service Provider. They are companies that help connect you to the Internet. For example, your mobile network providers like Glo, MTN, etc.
The answer to the above question is yes.
Your ISP knows the IP address of the VPN server you are using, but they do not know the websites you are visiting or the content of the data you are sending.
What Are the Security Implications of Using a VPN?
The number-one security implication of using a VPN is trust. Whenever you use a VPN, you are entrusting your data and privacy to your VPN provider.
Believing VPN providers, in their own words, of no logs and absolute privacy, is a huge decision and a risk you will have to decide whether to take or not. So, it is important that you choose a VPN provider you can trust.
Another thing you should note is that if your VPN provider is not secure, it will put your data in danger. If they are hacked, you are also hacked indirectly, especially when they keep logs of your data.
It is advisable that you use a trusted VPN provider, either open-source or paid. Better still, avoid using a VPN to run sensitive transactions like bank transactions on the internet.
Suggested Post: How To Enable Secure DNS Or DoH On Your Browsers For Security and Privacy
What is a proxy server?
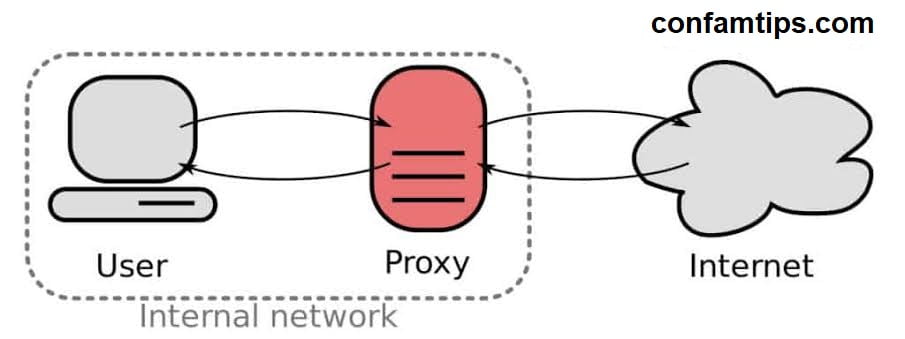
A proxy server is an intermediary server that sits between you and the resources you are requesting from the Internet. Just like a VPN, it makes the request on your behalf using its IP address.
With that being said, you should now understand that the proxy server’s main purpose is to make you anonymous. Proxy is not after encryption. It acts as a gateway between the user and the Internet. It can also be used as a firewall or resource access filter.
How does a proxy server work?
The role of a proxy server is similar to that of a VPN, except for the encryption part.
Let’s assume you are trying to visit your bank’s website with a proxy turned on in your browser. The moment you send the request, it will first go through your proxy server, which will forward it to your bank server. Therefore, your bank will be seeing the IP address of the proxy server you are using and not your device’s IP address. This will also change your location to that of the proxy server.
Related Post: IP Address- What Can A Hacker Do With it?
Proxy servers, unlike Tor networks, which are slow in connection, speed up your internet access. This is because proxy servers help cache websites you visit and deliver them to you in your subsequent request.
Differences Between Proxy Server and VPN
One key difference between VPN and proxy servers is that VPN acts on the system level. This means that once you turn on VPN on your computer, every app makes its request through it, while proxy acts on the application level. That means that when the proxy is turned on, it doesn’t impact all the apps on the phone or computer. For your browser or apps on your computer or phone to use a proxy, you will need to turn on proxy in those particular app settings.
Another difference is encryption. Proxy servers do not encrypt your request by default, while VPNs do. Encryption is part of the function of a VPN. The role of a proxy server is just to disguise your IP address to prevent hackers from stealing it, unless configured otherwise.
Does Your ISP Know You Are Using Proxy?
The answer is yes.
Not only that, but they also know the website or server you are visiting and the content of the data you are transferring if it is not encrypted with HTTPS. The proxy makes you anonymous only to the server or website you are making requests from.
What Are the Security Implications of Using a Proxy Server?
The number one security risk of proxy is personal data exposure. The proxy server you use will have a lot of information about your internet traffic. They can also get hold of your login credentials if they were delivered through HTTP. You must trust the proxy provider before you use them.
Remember, a proxy does not prevent your ISP from knowing the websites you visit. If your proxy provider server is hacked, your data can be stolen through the process.
What is the Onion Server?
The onion servers are servers operated by volunteers that run their Tor hidden services. You can turn your personal computer into an onion server if you want.
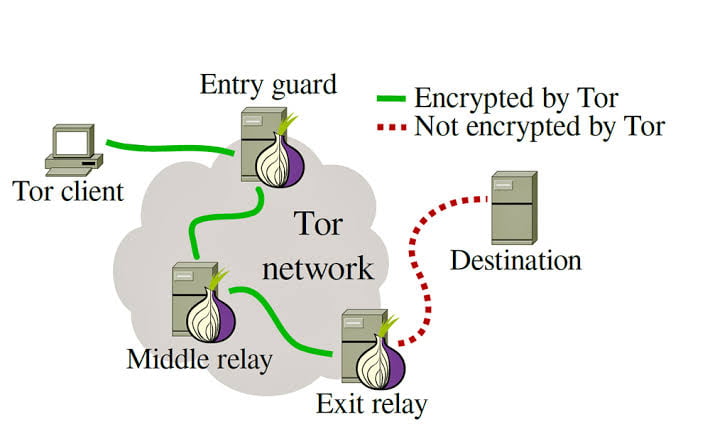
The Tor network is a service designed solely for anonymity. Traffic going through the Tor network is encrypted with layers of encryption, which will be pilled off as the packet travels through the network nodes. This is where the name onion comes into play.
Related Post: Dark Web Simplified-All You Need To Know And How To Access It
How Does the Tor Onion Network Work?
The two networks work like VPN and proxy when it comes to hiding your IP address, but the method differs. In VPN and proxy, your traffic passes through one VPN or proxy server to get to its destination with one or no encryption layer.
In tor onion routing, your traffic is routed through at least three servers which decrypt your traffic as it progresses.
For example, if you want to access your bank website through tor network. Your request is first of all encrypted with an encryption layer up to the number of routing nodes it will pass through before it gets to its destination.
The first node has the capacity to remove or decrypt the first layer of encryption. It will only reveal to it the destination to forward the traffic to and nothing else.
The same will happen on all the other nodes until it gets to the final node which is known as the exit node. The exit node removes the final encryption. It will then reveal the destination of the request and the data you are transferring, but not your original IP address. The exit node is where the traffic leaves the tor network to your bank server.
When your bank sends back the response, it will still pass through the exit node back to you. Each node will now have to put back the encryption as they receive the packet. Now your tor client can decrypt the three layers of encryption to reveal the response.
Does Your ISP Know You Are Using Tor?
The answer is YES, except if you use tor with VPN. This will confuse your IPS that you are using a VPN instead.
The only thing your ISP knows while you are using the Tor network is that you are using tor and the amount of data you consume. But they can not tell what exactly you are doing with it.
What Is The Security Implications Of Using Tor?
The weakness of tor lies at the entry and exit node. Data transferred from the exit node to its destination is not encrypted. A hacker sniffing at that end might see and steal your login credentials. But they won’t know it is coming from your IP address.
Another risk from tor servers being volunteers operated. Hackers use this opportunity to infiltrate the network with their servers. This will make it possible for them to get your credential when they are randomly chosen as your exit node. When anonymity is your concern, tor is the best place to go.
One Mistake You Should Never Make While Using VPN, Proxy, and Onion Services
Never make the mistake of visiting a website you had been visiting using the open net with a VPN, Proxy, or Tor. It defeats the purpose of the service.
One common goal of VPN, proxy, and onion services is to prevent tracking on the internet by making you anonymous. So, visiting a Facebook account you created without a VPN or Tor with VPN or Tor does not in any way hide your identity. Any activity on the account will still be attributed to your IP and your tracking will still be possible.
Another mistake you should avoid is paying for services online using your credit card while you are using a VPN, proxy, and onion services. It is better you pay with services that protect your anonymity like Monero or Bitcoin.
Suggested Post: IP Address- What Can A Hacker Do With it?
What is Common With VPN, Proxy, and Onion Services?
One thing VPN, Proxy and Onion services have in common is anonymity. They all prevent the services you visit on the internet from knowing your IP address, thereby preventing tracking. Also, they help to disguise your location, this makes it possible for you to access prohibited content in your location.



