If you use the internet and you don’t know about these two things; then you are among the most vulnerable people on the internet.
Web links are among what makes surfing or browsing the web possible. You move from one webpage to another with the help of links.
So, understanding how links can be manipulated to harm or scam you is among the fundamentals of internet security.
The number one common thing everyone is expected to know about a link is how to identify a secure or encrypted link.
Secure links are those links that have HTTPS encryption enabled, so they will look like this https://example.com.
If you see a link that looks this way; http://example.com, please avoid it. Don’t click on it. Data transferred through such a link can be eavesdropped with a tool like Wireshark and read.
Look at the two addresses closely. The only difference is the “s” in the “HTTP“. If there is no “s” at the end of the Http like this “https“, please flee the link.
Suggested Post: URLs- How to Detect Scam and Malicious Link URLs
Remember, a secure or HTTPS enabled link does not mean a fraud or scam free link. Links owned by scammers or bad actors can also use HTTPS but are still not totally safe. But it is always more dangerous to visit an unsecured link.

The second thing you should know, is how URL link manipulation is done.
Link manipulation is used by bad actors or internet scammers to lure victims to giving out their sensitive information on a fake website.
Number one link manipulation that scammers or bad actors use is the subdomain trick. To know more about what domains are and the different levels of domains, you can read about it here.
Subdomain trick is a link manipulation trick where scammers or bad actors use a subdomain to confuse an internet user on where a link is taking or directing them to when clicked on.
Here are a few examples of URL link manipulation using a subdomain. Looking at these two web links below, where do you think this link will take you when you click on it?
https://facebook.com.example.com
https://firstbankpls.example.com
At first glance, you might think the first link will take you to Facebook and the second to FirstBank. That is not what happens, instead, you will be taken to the main domain example.com.
Looking at those links closely, you will understand that the facebook.com section of the first link is just the subdomain of the website example.com.
Subdomains are only part of the main domain. Those links take you to the subdomain section of the main domain.
Whenever you see a link, make sure you monitor the main domain not the subdomain, because that determines where the link is taking you.
If you see a link like https://google.abcz.com. Remember this link is taking you to the google section of the abcz.com website and not to google website.
I hope you now understand the subdomain. So, what do you think scammers or bad actors can achieve with link manipulation?
If bad actors can convince you that the second link comes from your bank by just adding firstbank as the subdomain of their website example.com.
They can deliver to you a webpage that resembles your bank website and lure you into typing your account login details.
Remember, mirroring a website is not hard to do, bad actors will only have to reprogram the backend of the website, and use it to steal the details you enter on the website.
The second kind of link manipulation is the subdirectory trick.
This is similar to the subdomain trick, but this time bad actors are using subdirectory instead.
This is how the link manipulation looks.
https://example.com/ng/google.com/support.
Looking at this link on the browser, you might think you are visiting the Google support website without knowing you are just visiting a subdirectory in the example.com website.
Always remember, anything you see after the “/ ” symbol on a link is a subdirectory of the main domain, not the main domain itself. So, don’t see them as the website the link is taking you to. Rather they are just a folder on the main domain.
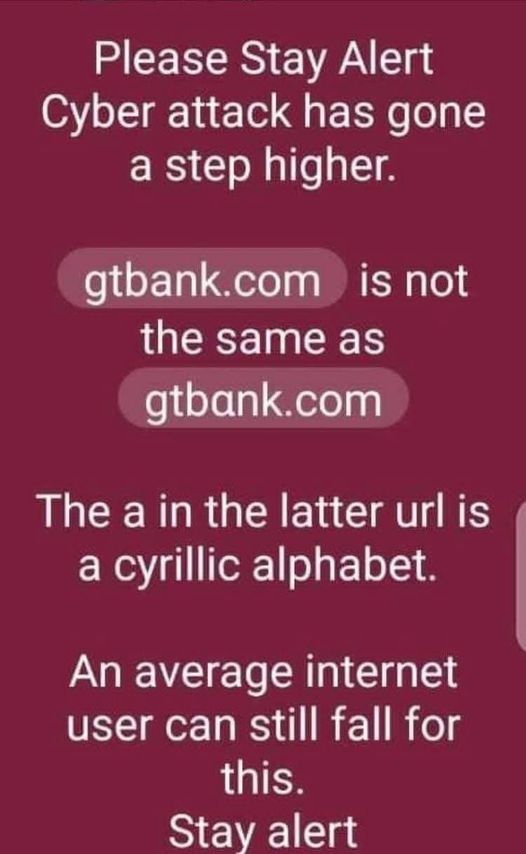
The third link manipulation we will look at is the domain name homograph.
IDN homograph is a situation where domain names look alike but they are not the same.
This is another intent to confuse users on where a link is taking them. A link like https://rnicrosoft.com might confuse you to think it is from Microsoft if you didn’t look closely before clicking. Or an address like https://paypaI.com might convince you to think it is a PayPal address, while the last alphabet is capital “i” instead of “L”.
If you find our post helpful and wish to be reading from us, please subscribe to our newsletter at the bottom of this page and remember to share this blog with your friends and family.
Suggeted Post: Website Security Scan-How to Check if a Website is Safe
Your views are important to us, feel free to share them on the comment box below.