In today’s connected world, your home Wi-Fi network is the gateway to many devices—from computers and smartphones to smart TVs, IP cameras, voice assistants, and even connected appliances.
Ensuring that this gateway is secure is crucial for protecting your personal information and keeping hackers at bay.
Many of us have been in the situation where we just open a brand new router, plug it in, set the SSID name and password, and voila! Our job is done.
This guide will walk you through practical steps to secure your home Wi-Fi network, making it harder for unauthorized users to access your internet connection and data.
Steps to Secure Your Home Wi-Fi Network
1. Encrypt Your Network
- What is encryption? Encryption is a process that scrambles the data sent over your network, making it unreadable to outsiders. This is a crucial step in preventing unauthorized access.
- How to Encrypt Your Network: Access your router’s settings and update the security protocol to WPA3 Personal, the latest and most secure encryption standard. If your router doesn’t support WPA3, use WPA2 Personal. Avoid older protocols like WPA and WEP, as they are outdated and vulnerable to attacks.
- What If Your Router Doesn’t Support WPA2 or WPA3? Older routers may not have these options. In this case, check if a firmware update is available for your router, which might add these newer encryption options. If an update isn’t available, consider investing in a new router to enhance your network security.
2. Change Default Router Settings
- Why Change Default Settings? Many routers come with default admin usernames, passwords, and network names that are publicly known, making them easy targets for hackers.
- How to Change Your Settings: Log into your router’s administrative panel (usually accessed by entering your router’s IP address into a web browser). Change the default username and password to something unique and strong. Also, change the SSID (network name) to something that doesn’t reveal the router brand or your personal information.
The Default Router Password Dilemma
To make setup simpler, routers come with default admin usernames and passwords, like “admin/admin” or “admin/password.” While manufacturers find this strategy useful, it puts unsuspecting users at great risk of security breaches. Think of it as similar to hiding your house keys under the front door welcome mat.
With a default password, your home network becomes an open invitation for cybercriminals. These digital intruders can easily gain access to your router, giving them control over your internet connection.
Why Do Users Leave Default Passwords Unchanged?
Understanding why so many users fail to change their router’s default admin password is key to addressing the problem. Several factors contribute to this issue:
- Lack of Awareness: Many users simply do not know the risks associated with leaving the default password unchanged. They may not understand how easily these credentials can be found online or the extent of the damage that can be done if their router is compromised.
- Fear of Technical Tasks: Some users are intimidated by the idea of accessing and changing their router’s settings. They fear that they might “break” something or make their network unusable if they alter the default settings.
- Perceived Inconvenience: Changing the default password may seem like an unnecessary or time-consuming task, especially if the user is not experiencing any immediate problems. As a result, they may postpone the task indefinitely.
- Assumption of Safety: Users often assume that their network is secure simply because it is working fine or because they have set a Wi-Fi password. They may not realize that the admin password is a separate entity that controls access to the router’s settings.
Contact Us for Your Home Cybersecurity Needs
The Consequences of Neglecting Changing Your Default Router Password
Neglecting changing your router default password can make it easy for attackers to have access to your network. Once in, the possibilities for mischief are endless. They can eavesdrop on your online activities, steal sensitive information, redirect your internet traffic to malicious sites, or even use your network to launch attacks on others.
But the dangers don’t stop there. A compromised router can also serve as a gateway for hackers to infiltrate other devices on your network, such as computers, smartphones, and smart home gadgets. This can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and privacy breaches.
So, what can you do to protect yourself?
The answer is simple: change your router’s default password immediately. Most routers allow you to access the admin settings by typing a specific IP address into your web browser, or you can get your default gateway IP address through your computer command line by typing the “ipconfig” command on Windows or “netstat -nr/grep default” on Mac.
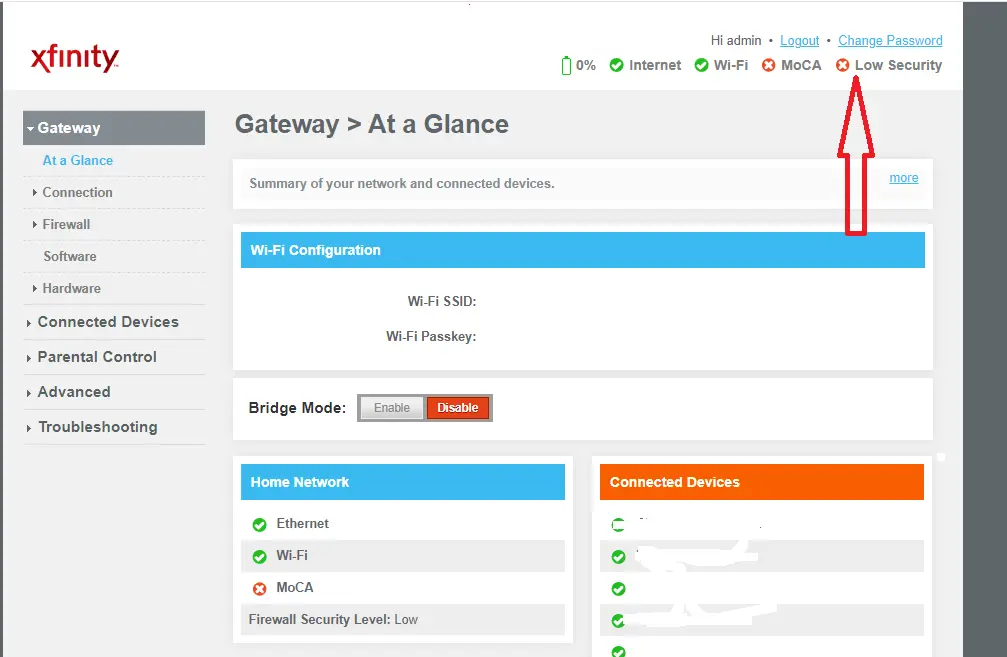
Once logged in, you can easily change the password. Be sure to choose a strong, unique password that combines upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols if allowed.
3. Keep Your Router Firmware Updated
- Why Updates Matter: Router manufacturers release firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities and improve performance. Regularly check the manufacturer’s website for updates, or enable automatic updates if available.
- How to Update: Visit the router’s settings page and look for a firmware or update section. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to download and install updates.
Cybersecurity tips for personal awareness
4. Disable Unnecessary Features
- Remote Management: This feature allows you to access your router’s settings from outside your home network. While convenient, it poses a security risk. Disable remote management to prevent unauthorized access.
- Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS): WPS is designed to make it easier to connect devices to your network, but it can be exploited by hackers. Turn off WPS to enhance your network security.
- Universal Plug and Play (UPnP): UPnP allows devices to discover each other on the network, which can be useful but also risky. Disable UPnP to prevent malware from spreading across your devices.
5. Enable the Router’s Built-in Firewall
- What is a Firewall? A firewall is a security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. Most routers have a built-in firewall that helps protect against malicious attacks.
- How to Enable: Check your router’s settings to ensure the firewall is enabled. If it’s not, turn it on to provide an extra layer of protection.
Ensure that all devices connected to your network have up-to-date antivirus software, strong passwords, and the latest operating system updates. Secure devices make it harder for hackers to gain access to your network.
FAQ
1. How often should I change my Wi-Fi password?
It’s a good practice to change your Wi-Fi password every few months, especially if you have shared it with multiple guests.
2. What should I do if I suspect someone is using my Wi-Fi without permission?
Check the list of connected devices in your router’s admin panel. If you see unknown devices, change your Wi-Fi password immediately and consider enabling a guest network for future visitors.
3. Can I use a VPN to secure my home network?
Yes, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) can add an extra layer of security by encrypting your internet traffic. Some routers support VPN configurations, or you can use a VPN on individual devices.
4. What should I look for when buying a new router?
Look for routers that support WPA3 encryption, have built-in firewalls, and offer features like guest networks and automatic firmware updates.
5. Are there any apps that can help monitor my home Wi-Fi security?
Yes, there are several apps available that can monitor your network for suspicious activity, check for vulnerabilities, and alert you to potential security threats. Research and choose one that fits your needs.